Amazon is everywhere. There’s no getting around it: From small sellers to large enterprises, getting your products noticed — and purchased — means you need a marketing strategy that lets you make the best use of this online ecommerce behemoth.
Today’s consumers use Amazon as their first point of contact for finding almost any type of product information. In fact, 63% of online shoppers go to Amazon to start searching for products. But with so many products available from multiple sellers with varying shipping options and discounts, it’s easy for your brand to get passed over by potential buyers.
Bottom line? Amazon is the ecommerce heavyweight. Love it or hate it, you need a market strategy that helps your brand stand out among the thousands of others all vying for consumer attention. That’s why we’ve built this guide — to help you build a profitable marketing strategy and succeed in the sales jungle that is Amazon.
Bookmark this post for later, and use the chapter links below to jump ahead to sections of interest.
1. Create an Amazon Advertising strategy.
Generally speaking, an Amazon Advertising strategy consists of four components: Amazon reviews, SEO, affiliate marketing and social media marketing.
What is Amazon Advertising?
Amazon Advertising (previously Amazon Marketing Services) is a pay-per-click service similar to Google Ads: Brands only pay when potential buyers click on targeted ads. Designing the idea ad is critical to getting your brand noticed and generating sustained revenue.
There are three common types of Amazon Advertising ads: Product Display, Sponsored Product and Headline Search.
Product Display ads show up on the side or bottom of Amazon SERPs and along the side of related product pages. When clicked, Product Display ads lead to a product page.
Sponsored Product ads appear in the Amazon SERPs and on product pages before the product description.
When clicked, Sponsored Product ads lead to a product page.
Headline Search ads are the most customizable Amazon ad.
They appear at the top of Amazon SERPs and can include custom ad copy as well as link to a branded landing page on which you can feature custom navigation, branded imagery, and select products.
2. Develop an Amazon reviews strategy.
Customer reviews and ratings are important. They’re even more important in the world of ecommerce, where shoppers can’t physically see or touch a product before buying. In fact, recent data found that customers prefer not to engage with brands that have less than 3.3-star ratings.
Amazon recognizes the power of customer reviews, and — true to their buyer-first mindset — makes reviews a major part of each product page. Shoppers can view customer images, filter reviews by suggested keywords, search for content within reviews, sort reviews by stars, and review customer questions and answers.
As a seller, you should always prioritize reviews. They can make or break a shopper’s decision to purchase — and the more positive reviews your product has, the more likely you’ll turn casual interest into conversion.
Here are a few ways to do this ask your customers to complete one. Here are a few ways to do this:
- Include a thank-you note and review request in your product shipment
- Send a follow-up email with a review request
- Sell a commonly-reviewed product
It’s also worth noting that Amazon allows sellers to respond to reviews. This offers a great way to engage directly with customers, express gratitude for purchases, and quickly address issues or complaints.
3. Deploy an Amazon SEO strategy.
Let’s be clear: Amazon dominates the ecommerce market in North America. But it’s not just an ecommerce site — it’s also a search engine. And as a search engine, it has its own search engine optimization or SEO.
Amazon’s search engine is called A9. It operates on its own algorithm and comes with its own unpredictable updates, similar to Google. A9 is also similar to Google in another key way: Searchers (in this case, buyers) are its top priority.
This is great if you’re a shopper, but more challenging if you’re a seller.
Thankfully, there’s a simple rule for Amazon SEO strategy: Think like a buyer. This means optimizing your content for three things: Discoverability, relevance, and sales. In other words, you want shoppers to see, click, and buy your products.
Create listings that reflect commonly-used keywords for your product category and make sure your product pages provide up-to-date, relevant information that offers direct value to buyers.
4. Integrate an Amazon affiliate marketing strategy.
Product round-ups published by popular blogging sites make it easy to scan a list of top-rated products and find direct links to Amazon.
But how do these products end up on the list? Affiliate marketing. Affiliate marketing is effectively an exchange: In return for your product being published/mentioned/shared, you pay a small fee to the affiliate site if readers click and purchase. It’s a win-win scenario that helps you drive sales and collect positive reviews. It’s also a critical way to build brand awareness, especially if the affiliate site generates a substantial amount of web traffic.
👉🏼HubSpot Tip: Tap into Amazon’s Affiliate Program. It’s free and easy to use and immediately connects you with approved affiliates.
5. Expand your Amazon social media marketing strategy.
It’s a good idea to expand your marketing efforts with a social media strategy that ties back to your Amazon page.
Here, the goal isn’t to create purely promotional Facebook, Twitter or Instagram accounts but instead cultivate a brand identity that offers value to your consumers with interesting posts, facts and links. You can also use your social media to share product updates, announce sales and giveaways, and invest in some paid advertising.
Here, the key is balance: Too much branded content and you’ll lose customer interest. The occasional mention and link to your Amazon page, meanwhile, can help you connect with prospective buyers and drive total sales conversions.
👉🏼HubSpot Tip: Share your social media accounts on your Amazon brand page and product listings to build your follower list.
1. Product Title
This is an Amazon product I actually purchased. You’ll see this example throughout the piece.
Your product title is a consumer’s first introduction to your product when browsing Amazon. While you should keep your titles concise, Amazon does allow up to 200 characters. Use this character limit wisely, though.
Here’s what we recommend including:
- Your brand name
- The product name
- Specific features (such as size, color, material, quantity, etc.)
- One or two distinguishing benefits or values
Here are some of Amazon’s title formatting rules:
- Capitalize the first letter of every word (except for words like “and”).
- Use “and” instead of “&” and numerals (“10”) instead of written numbers (“ten”).
- Don’t put pricing, seller information, promotions, and opinion-based copy (words like “best” or “leading”) in the title.
- Leave out details like color or size if irrelevant to the product.
Your title is prime real estate for two things: Product information and keywords. For most products, these are one and the same, but some sellers opt to add a few additional keywords to increase their chances of popping up on Amazon SERPs.
Ultimately, your title should match the words shoppers use to discover your product and educate them on your product before they get to your page.
👉🏼HubSpot Tip: Use tools like Merchant Words and Simple Keyword Inspector to research potential keywords and their search volume.
2. Product Images
While your titles communicate your product information, consumers often use your images to decide whether or not to further explore your product page. This is especially critical on a long list of Amazon search results — the right product imagery can help your product stand out from the crowd.
Once a shopper visits your product page, however, imagery is even more important and can dictate whether a consumer makes a purchase not.
Amazon allows up to nine product images, and we recommend using all of them with a simple caveat: Only if you have nine high-quality, relevant images.
While Amazon requires your main product image needs to be on a plain, white background, here are some tips for your other eight product images:
- Capture your product from different angles.
- Show your product being used or worn by a real person (not a mannequin or computer-generated human).
- Include content submitted by real customers — and make note of that on the image.
- Upload images that include charts, lists, or competitor comparison tables.
Amazon also offers shoppers the ability to zoom into each image. As a result, your product images should be at least 1,000px x 1,000px to ensure images don’t become fuzzy or distorted when customers zoom in.
👉🏼HubSpot Tip: Test your product images to see which one converts more shoppers (like an A/B test). To do this, record your sessions, sales, conversion rate, and revenue over the course of a week or month — and make a note of which image was set as the main image. Then, change the image and capture the same data.
3. Product Key Features (Bullet Points)
If a consumer makes it past your product title, images, price, and purchase options (if applicable), they’ll find your product key features, which take the form of bullet points. These bullet points allow you to go more in-depth about your product’s features, benefits, characteristics, and details.
Successful Amazon sellers use these bullet points to expand on features and benefits and to address common questions, misconceptions, or issues.
Here’s how we recommend you approach your product key features list:
- Write a paragraph for each bullet and include two to four sentences or phrases that are relevant to that bullet’s topic.
- Capitalize the first few words of each bullet to emphasize the feature, benefit, or question you’re addressing.
- Treat these paragraphs as you would an advertising campaign. This copy could be the key to converting page visitors.
- Avoid wasting space on information that’s obvious from product images or mentioned in your product title.
- Keep them simple. Write a paragraph and then edit it, set it aside for a few days and then edit again. Short and to the point is the goal.
👉🏼HubSpot Tip: Look at reviews, complaints, and FAQs to learn what your customers love and not-so-love about your products. Proactively include and address these points in your list.
4. Product Description
If a consumer makes it to your product description, you can assume they’re on the cusp of making a purchase. How do we know that? Consumers have to scroll down a bit to find it.
Seriously. They have to scroll past Amazon ads, sponsored products, and other featured information. If they make it to your product description, they’re typically expecting to learn more about your product and finalize their purchase.
This makes your product description the ideal place to expand on your product bullet points, address some lesser-known features and benefits, and perhaps include some more images of your product. Additionally, consider listing details that set your product apart from competitors, such as specific construction methods, particular materials or interesting use cases.
Amazon allows the use of basic HTML markup in this section — including bold, italics, and page breaks — so utilize these to avoid publishing one big, boring paragraph of information.
👉🏼HubSpot Tip: Utilize Amazon’s A+Content option to make your content more scannable, professional, and consistent with your overall branding. We cover how to do this next.
5. Product Price
Setting the right price is critical for reliable sales conversions.
Start by determining your lowest possible sales price. This is effectively a “breakeven” price that includes the costs to produce your product along with money spent on marketing and any fees taken by Amazon — which vary depending on the type of item you’re selling, often between 8-20%.
For example, if these costs together total $10, this is your minimum price. You won’t make any money, but you won’t go out of business. While this can be a good starting point if you’re just breaking into the Amazon marketplace, your goal is to eventually sell products for as much as the market will bear.
To find your upper limit price point, do some research on similar, popular products on Amazon and see what they’re selling for. Next, determine how you want to position your brand — are you looking to lead the lower-cost market, or hoping to capture premium prices. Both are possible but require different approaches.
If you’re looking for premium prices, opt for whole numbers such as $50 or $100. For a lower-cost approach, go with a “99 cent” approach, such as $9.99 or $29.99.
6. Amazon A+ Content
The A+ framework provides pre-built templates that allow you to add additional features to your product descriptions, such as banners, tables, bullets, and interactive images and copy.
The image above is the “Comparison Products” template, which is one of the most popular and functional templates for A+ Content. It’s now available via both Vendor and Seller Central and offers a great way to visually showcase how your product stacks up against the competition.
Factors that Can Increase Your Amazon Product Sales
1. Direct Marketing
A lot of Amazon marketing takes place within the platform (through advertising and SEO) but some sellers follow traditional direct marketing methods, too. While they require extra work, they can be beneficial for creating loyal customers and eventually bringing business off of Amazon to an ecommerce site, or driving users from social media sites to your Amazon account.
Direct marketing methods skip the middleman to present information about your brand directly to prospective customers. This includes the use of emails, text messages, phone calls, sales offers or newsletters.
Note: Be sure to read through Amazon’s prohibited seller activities and actions to ensure you remain compliant. The biggest takeaway? All direct marketing efforts must be done with the informed consent of customers — unsolicited contacts could place your brand at risk of removal from the Amazon marketplace.
2. Email
Follow-up emails are a great way to engage with customers and get feedback that could help make your brand even better. Start by asking buyers if they consent to email contacts or surveys after their product purchase.
If yes, make sure to take their feedback to heart, both by responding to their emails with a thank you and correlating their response with other emails to see if a pattern emerges around product price, quality or another characteristic.
👉🏼HubSpot Tip: If you decide to do email marketing for your Amazon products, don’t forget to ask subscribers if they want to opt-in!
3. Website
Amazon offers a well-recognized starting point for your brand, but many sellers are also branching out into brick-and-mortar stores or more niche marketplaces such as Etsy.
While Amazon can help you be discovered and subsidize your shipping and customer support cost, creating a separate website can help build your brand beyond Amazon and aggregate customers and email subscribers of your own.
👉🏼HubSpot Tip: If you have no interest in building and managing an entire website, create a simple landing page to start. This will at least give your brand an online identity outside of your Amazon store and provide another place to collect emails and promote your social media.
4. Shipping
One of the biggest draws of Amazon is fast, free shipping for Prime members. If you’re looking to compete in this massive marketplace, you’ll need to consider shipping costs, speed and conditions for buyers before you set up your store.
While smaller businesses don’t have the economies of scale that allow them to offer 2-day free shipping, it’s often possible to offset the costs of shipping once order values are large enough. As a result, it’s worth doing the math to determine where it makes sense for your brand to offer free shipping for consumers — this might be $50, $100 or $150 worth of products purchased.
Best bet? Set your minimum free shipping cost just above your breakeven point using a whole number. For example, if $129 worth of products purchased makes it worth your while to offer free shipping, set the minimum amount to $150. This helps generate slightly more profit and can help convince users to add one or two more items to their cart in order to avoid shipping costs.
Understanding Amazon Analytics
Amazon analytics provides a snapshot of what consumers are searching for, what they’re buying and how often they’re purchasing the same item. Called “Brand Analytics”, these metrics are available to sellers directly responsible for selling their brand in the Amazon store.
Brand analytics are found under the “Reports” tab in Seller Central.
Brand Analytics, Explained
There are six brand analytics categories. Let’s break down each in more detail.
1. Amazon Search Terms Report
The Amazon Search Terms Report shows the most popular search terms in the Amazon store over a specific period and the top three products that customers click on after searching for a specific term. This can help your brand better target keyword usage over time.
2. Demographics Report
The Demographics Report provides information about buyers of your product that they’ve consented to share — including age, household income, gender and marital status. This allows you to see the impact of your marketing campaigns and adjust target consumer bases as required.
3. Item Comparison Report
This report shows the top five products most frequently viewed on the same day as your brand’s products to help you identify your top competitors and see what they’re doing differently.
4. Alternate Purchase Report
The Alternate Purchase Report shows the top five products that customers purchased most frequently instead of your products. Effective use of this report can help identify areas where your marketing strategy may be coming up short.
5. Market Basket Report
The Market Basket Report shows the top three products most frequently bought at the same time as your products. This can help your brand identify key add-on product opportunities to help bolster total sales.
6. Repeat Purchase Behavior Report
The Repeat Purchase Behavior Report shows the total number of orders for their products along with the total number of unique customers. This makes it possible to zero in on specific user characteristics that may influence repeat buying and help inform long-term marketing strategy.
You’re Now the King 👑 (or Queen) of the Jungle
While the Amazon platform seems daunting, the right marketing strategy can help your brand see sustained sales success.
First, develop a solid Amazon marketing strategy. Next, make sure your product pages stand out from the crowd and ensure you’re taking take every opportunity to increase total sales. Finally, use Brand Analytics to pinpoint areas of improvement across your brand.
The result? Your Amazon products will meet consumers wherever they are — whether they’re researching products, comparing prices, or looking to buy — and help get them where they need to go: Your checkout page.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in April 2019 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
![]()








![New Data: Instagram Engagement Report [2021 Version]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/9294dd33-9827-4b39-8fc2-b7fbece7fdb9-3.png)



 37. More than 25 million businesses now use Instagram to reach and engage with audiences. (
37. More than 25 million businesses now use Instagram to reach and engage with audiences. (

![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-2.png)



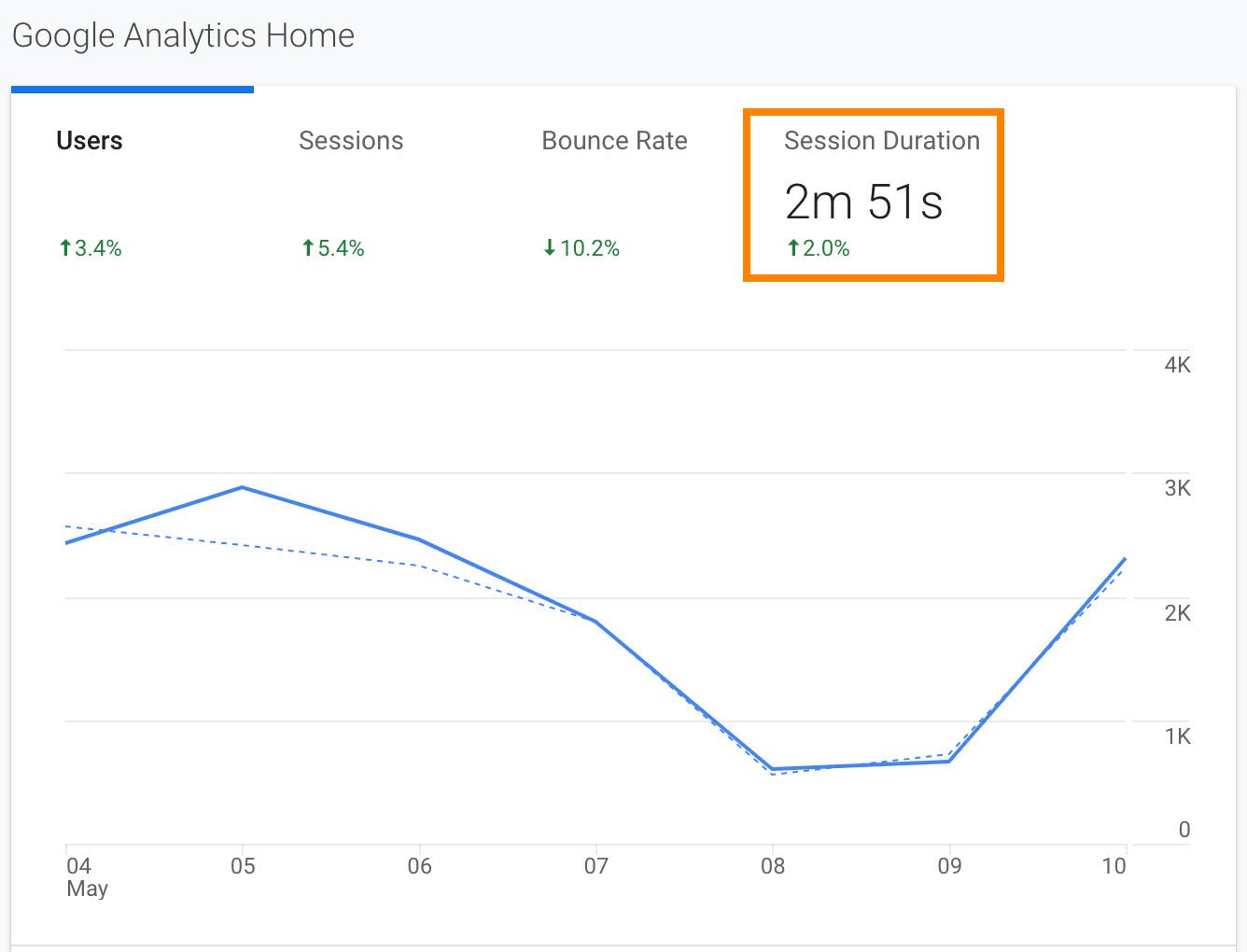 If you want to explore “Average Session Duration”, or dwell time, for individual landing pages or blog posts, you’ll want to click “Behavior” on the left side of the screen, and then “Site Content” > “Landing Pages”:
If you want to explore “Average Session Duration”, or dwell time, for individual landing pages or blog posts, you’ll want to click “Behavior” on the left side of the screen, and then “Site Content” > “Landing Pages”: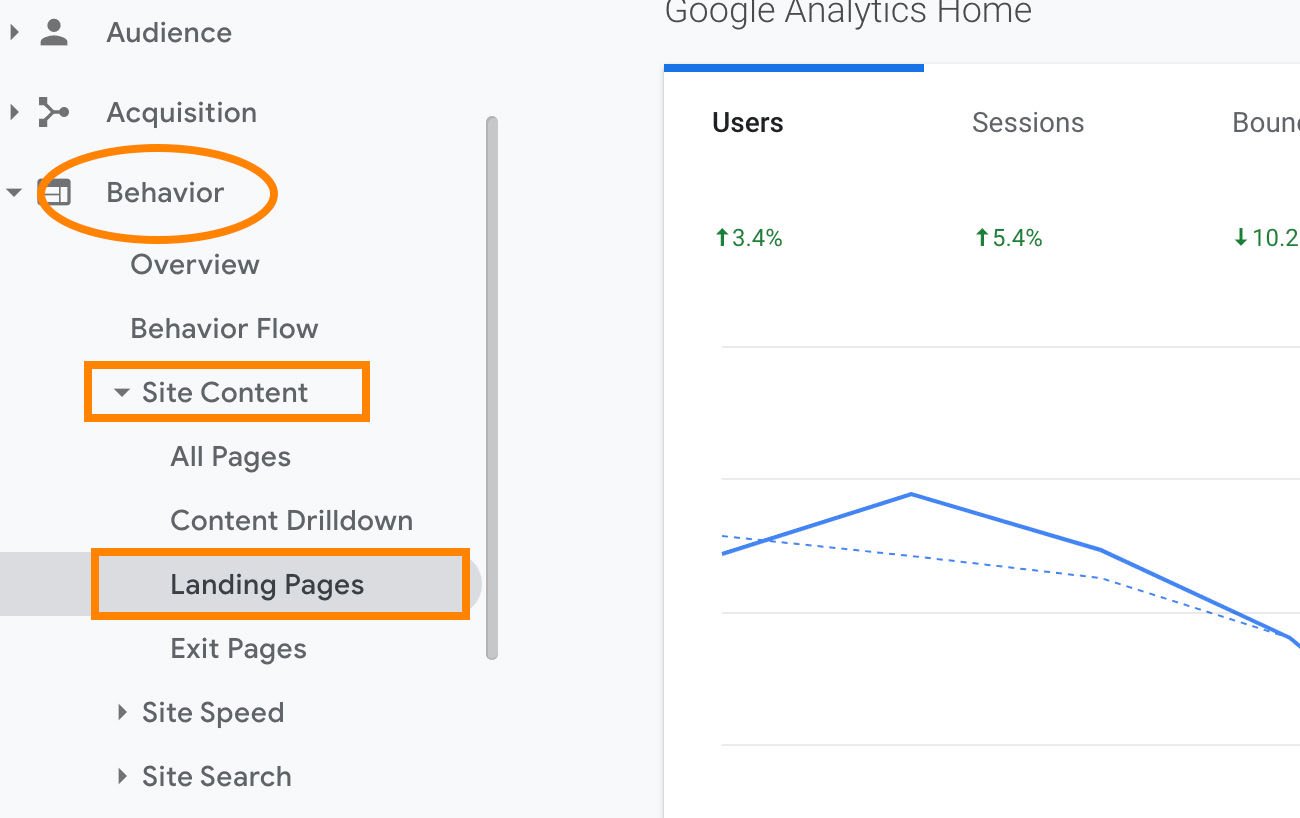
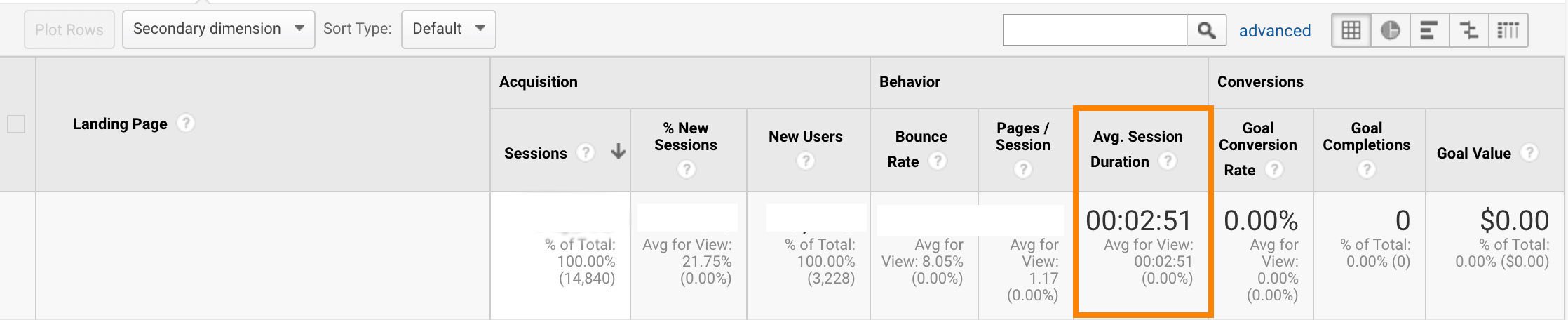 It’s important to note — “Average Session Duration” can depict dwell time, but the two aren’t the same. Dwell time can only come from the SERPs, whereas Average Session Duration might also measure someone’s time on-page after they’ve arrived from another landing page, social media page, or clicked on an email link.
It’s important to note — “Average Session Duration” can depict dwell time, but the two aren’t the same. Dwell time can only come from the SERPs, whereas Average Session Duration might also measure someone’s time on-page after they’ve arrived from another landing page, social media page, or clicked on an email link.
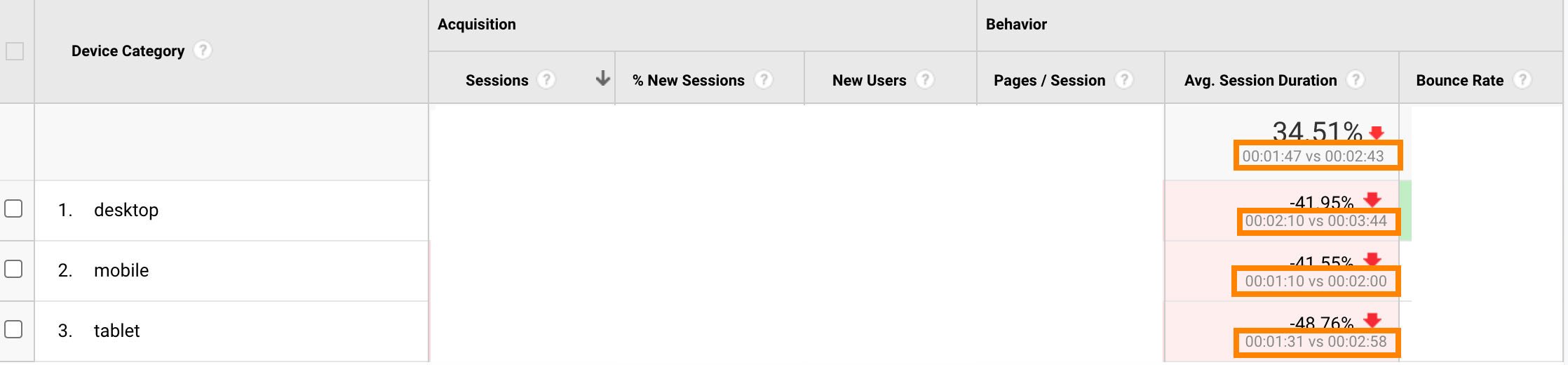 Most marketers agree that it’s rare to see average session duration times over 10 minutes or less than one minute, so if you’re looking for a goal, between 2-4 minutes is where the average typically lies.
Most marketers agree that it’s rare to see average session duration times over 10 minutes or less than one minute, so if you’re looking for a goal, between 2-4 minutes is where the average typically lies.
![→ Free Templates: How to Use YouTube for Business [Download Now]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/b33cfd44-133a-49e3-a943-086c5679d485-1.png)

![→ Download Now: Free Product Marketing Kit [Free Templates]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/08b5e1f4-5d26-405b-b986-29c99bd0cb14.png)

![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-1.png)





![→ Download Now: The Beginner's Guide to Email Marketing [Free Ebook]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/53e8428a-29a5-4225-a6ea-bca8ef991c19-1.png)
