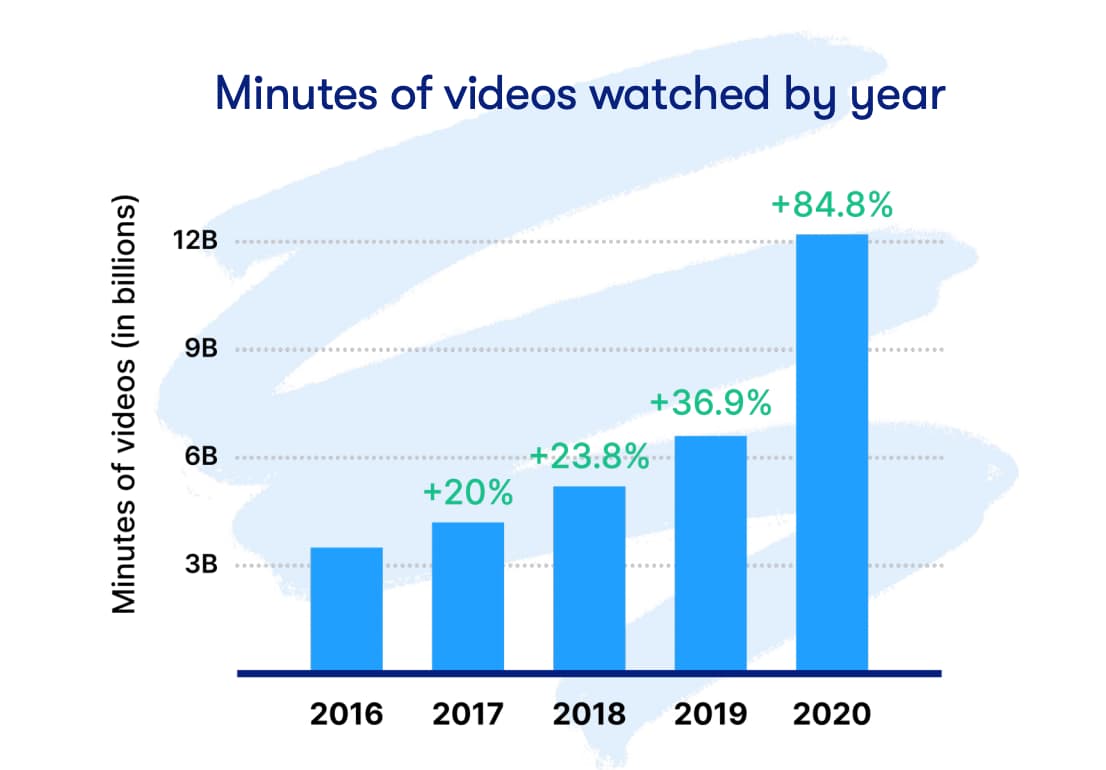
In 2020, 42% of people used social media channels for product research.
With younger generations getting more and more connected to social media, the amount of product research done on these platforms is likely to grow. In fact, 16 to 24-year-olds already conduct more product research on social than on search engines.
Throughout the past few years, social media channels have embraced their new role as product research channels, devoting certain areas or features of their platforms to showcasing brands and products.
For example, Facebook Ads is considered an alternative to Google Ads, YouTube is a go-to site for learning about new products (and how to use them), Instagram offers Shoppable posts, and Reddit users regularly participate in discussion threads about products and brands. And let’s not forget Pinterest, which continues to position itself as a tool for advertisers by improving its ad software.
With all the social media platforms and product marketing opportunities out there, it might be hard to drill down which platforms are key to your marketing strategy.
By now, you might be on all the major social media platforms. But, as they expand and evolve, you might still wonder which you should focus your time and efforts on if you’re selling a physical product. To determine this, it helps to find out which social channels your specific audience is using, and then create strategies that meet them where they are on their preferred platforms.
To learn more about the social networks people prefer to surf for product research, I conducted a poll of 304 people using Lucid Software.

Why is shopper research important?
Shopper research is critical for a better understanding of the customer journey from initial searches to website visits and eventual purchases. The advent of digital- and mobile-first interactions has made this research even more important as the customer journey now includes multiple paths and touchpoints from start to finish.
For example, prospective buyers might hear about your brand from a friend, do their research on social media, and then interact with your ecommerce store through their mobile device. Understanding all touchpoints along this journey can help companies create more seamless and streamlined experiences for consumers and increase overall ROI.
Shopper Insights Reveal Social Media Research Habits
Source: Lucid Software
At first glance, the survey data seems simple: Facebook is far and away the market leader when it comes to product research and eventual purchasing, followed by YouTube.
But that’s not the whole story. Part of the reason Facebook and YouTube rank so highly is because of their installed user base — for example, Facebook has three times the user base of Instagram, despite being owned by the same company.
It’s also worth noting that while Facebook marketing appeals to a broader audience, volume alone doesn’t guarantee conversion. Users on Pinterest and Reddit tend to be much more engaged with their social community — meaning that if your brand can capture their attention you can create substantive consumer loyalty. LinkedIn, meanwhile, relies on authenticity and authority to inspire confidence, while Twitter is all about what’s trending right now.
Here’s a breakdown of the data:
- Facebook: 51%, 155 people
- YouTube: 30%, 91 people
- Instagram: 6%, 18 people
- Pinterest: 6%, 18 people
- Reddit: 4%, 12 people
- LinkedIn: 2%, 6 people
- Twitter: 1%, 3 people
Facebook
Facebook has a whopping 2.7 billion active daily users and has been around since the early 2000s. Its audience includes multiple age groups and spans the globe, making it a solid place for most brands to market themselves.
When it comes to marketing your product, you have many free and paid options on Facebook. Here are a few examples of each.
Free Promotion
By now, you probably know that any company can create a Facebook Business Page. Once you create a business page, you can share posts about your products and offerings. If you have happy customers, you can even ask them to review your business on Facebook so prospects researching you can see how you’ve pleased your customers in the past.
Aside from creating a page to highlight your brand, you can also post your products in Facebook’s Marketplace. Marketplace listings can include product shots, pricing, product specifications, and purchasing information. Although individual users often use the Marketplace to sell items they no longer want to other people, Facebook Business pages are also eligible to use this feature.
You should also consider talking about your products or offerings on Facebook Stories. This might take a little extra effort because it will require you to film or create content in the Story format, but it can help you better connect with prospective buyers who want a better sense of what your brand is about.
Paid Promotion
Because Facebook’s feed algorithmically favors posts from individual accounts over businesses, you might decide that you want to put money into Facebook Ads.
Facebook Ads has a solid track record. It’s estimated that 10 million businesses were advertising on the platform in 2021.
With Facebook Ads, you can create advertisements with a certain goal in mind, such as conversions or in-store foot traffic. The detailed ads software also allows you to target specific audience demographics.
As a Facebook advertiser, you can either promote a post you’ve already created to ensure that it shows up on feeds of users in your demographic, or you can create native ads that might show up in feeds or on Facebook’s sidebars. While promoted posts look like an average post with a simple tag stating they’re promoted, the native ads look more like traditional ads to make it clear to users that the content they’re seeing is paid for.
If you want to launch video-based ads, Facebook also allows you to promote video content or buy in-stream ad placements that appear in Facebook Live videos or longer videos that other users have uploaded.
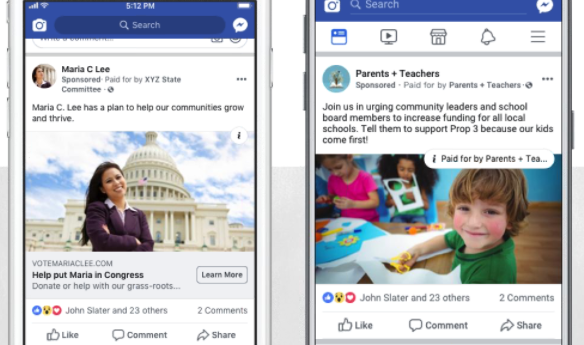
YouTube
If how-tos or video tutorials are part of your content marketing strategy. YouTube will be a natural fit for your brand. This is because YouTube users are three times more likely to prefer watching a YouTube tutorial video compared to reading the product’s instructions.
More and more companies are taking notice of YouTube’s product marketing opportunities. It makes sense, since 70% of viewers say they’ve made a purchase after seeing a brand on YouTube.
With a branded YouTube channel, you can publish video content such as demos, tutorials, or customer testimonial videos that give insightful details about why your product is valuable. By filming your own videos, you can insure that you’re highlighting all the great aspects of your product that make it stand out from its competitors.
Alternatively, if you don’t have time to create your own videos, sponsoring an influencer’s content, tutorial, or review related to your product allows you to tap into that content creator’s audience as they tell their followers more about your offerings.
Aside from creating your own account or hiring an influencer to give a review or tutorial, you could also consider paid advertisements. YouTube offers a few ad styles including TrueView, Preroll, and Bumpers.
These ads allow you to submit a short video ad to YouTube which is then placed at the beginning or in the middle of videos with metrics and demographics that match your brand’s target. To learn the ins and outs of setting up an ad and determining which style is right for you, check out this guide.
Instagram
Although Instagram ranked in third place in the poll above, you shouldn’t disregard it — especially if you’re targeting Gen-Z or millennials who make up the platform’s primary audience.
For years, Instagram’s visual layout has made it a hot spot for influencer marketing. Influencers regularly post sponsored photos and videos about their experiences with products. Like YouTube, these influencers also regularly publish video posts or Stories that present tutorials, reviews, and unboxings related to a product.
Aside from influencer marketing, many brands also promote their products on Instagram Stories, Instagram Live, and through standard video or photo posts on Instagram Feed.
Here’s an example where Kylie Jenner, the CEO and Founder of Kylie Cosmetics, films a Story-based product tutorial for her company’s Instagram account:
Along with free strategies, Instagram now offers Shoppable posts. With Shoppable posts, you can promote a product in an Instagram post that links to your Facebook Catalog. Here’s an example of what a Shoppable Post looks like:
To be eligible for Shoppable posts, you must have an Instagram Business page that’s linked to a Facebook Catalog. This feature is also only for businesses selling physical goods.
Here’s a blog post that goes into detail about how to use and optimize Shoppable posts.
Pinterest
Pinterest encourages people to pin image-based posts that inspire them to digital boards, mimicking the process of creating a physical inspiration board.
Because people come to this platform to be inspired to do something, such as travel or home decorating, they might find themselves pinning all sorts of product-oriented images to a themed board. For example, someone who wants to redecorate their office might create an “Office Inspiration” board and pin photos of furniture or decorative items that they’d like to buy.
Here’s an example of what these boards look like:
To make it easier for people to find your products, you could consider starting a Pinterest account and making a few boards to highlight your products. For example, if you’re marketing a travel company, you could make a board for each country that you offer packages to. On each board, you could place images of trip activities that link to your website.
Then, if someone is trying to plan a trip to a country you sell a package for, they might come across one of your posts and pin it to their own “Travel Inspiration” board.
To give you a real-world example of how brands use Pinterest, below is a Wedding Registry board created by Target which features images of products that a bride and groom might want to add to their gift registry.
Each of Target’s pinned images links to the company website so users can share the pin on their own Pinterest board, or click straight through the post to buy or register the product.
If you have an advertising budget, you can also consider launching pay-per-click ads on Pinterest. Pinterest Ads enables your posts to be seen by people in a specific demographic that matches your own. The platform also allows you to A/B test photos and target ads to Pinterest users on your contact lists.
Want to learn more about Pinterest Ads and effective experiments to run? Check out this blog post from a PPC and Pinterest expert.
Reddit
Reddit encourages users to create discussion threads in themed online communities, called subreddits. As the platform has evolved, many users have created both threads and subreddits devoted to talking about products, like fast-food restaurants or video games.
Below is an example of a subreddit, or online community, that Reddit users created to talk about all things related to Xbox One.
However, because comments with promotional language in them often get downvoted or buried in feeds by more engaging Reddit threads, you’ll need to be creative if you want to engage with audiences on this platform.
While you might want to keep an eye on Reddit or experiment with it, don’t put all of your time and resources into it — at least right now. As it evolves, the platform may become an easier platform to market your brand on, but at the moment, Reddit marketing strategies still require more brainstorming and time than tactics on other social platforms.
Although this platform has been called one of the “trickiest” for marketers to crack, some bigger brands have figured out how to reach the platform’s discussion-oriented users.
For example, some brands will create subreddits related to their product, while others will interact by commenting on threads related to their industry.
Aside from creating content for free on Reddit, you can alternatively pay into sponsored posts or ads, similarly to Facebook or Twitter. These ads will appear in a user’s feed or as a promoted comment in a thread or subreddit.
To learn more about the ins and outs of Reddit marketing, click here for tips and examples of how other brands have cultivated the platform.
LinkedIn
LinkedIn’s platform, which emphasizes networking and career-related chatter, might be well-suited for product marketing in B2B, academic, or professional industries. People who do product research on this platform might be looking for a service, tool, or software that can either escalate their careers or make their workdays easier.
If you’re marketing products like software, online courses, business-related publications, or anything that can help a professional or student do their job better, LinkedIn will be a great fit for you. However, if you sell more general, consumer-facing products like makeup or home decorations, you might want to put more marketing effort into other platforms on this list — like Facebook or Instagram.
While the professional nature of LinkedIn and its audience might not be suited for all brands, the platform still offers a variety of opportunities for brands to leverage it. For example, research shows that 80% of B2B leads come straight from LinkedIn.
LinkedIn is very similar to Facebook in that you can post about your product or service for free, or purchase ads or post promotion to get information about your business front and center on feeds. To see a few great ad examples, check out this post.
Image Source
Twitter
Twitter has approximately 200 million daily users from a variety of backgrounds, geographic locations, and industries. Its broad demographic might provide solid marketing opportunities to many different types of businesses. Because of its broad user base, you might want to create an account on Twitter and post regularly for brand awareness.
If you’re interested in video marketing, you can also experiment with Twitter’s live video feature and use it to film a tutorial or Q&A related to your product.
Aside from posting about your product for free, you can also pay into targeted ads or promoted tweets. Twitter claims that its advertising ROI is 40% higher than some other social channels.
While the ROI of Twitter advertising and its user base sounds promising, you might be wondering why it ranked so low on the poll shown above.
Ultimately, what might make Twitter rank last is its trend-oriented nature. The platform encourages people to connect with each other and post tweets or comments about current events, trending hashtags, or their thoughts on other specific topics.
Brands and product discussion are both prevalent on the platform, but users might go to Twitter to learn more about what’s going on in the world, rather than new products. When people are asked to pick which platform they do the most product research on, it’s not surprising that Facebook or YouTube might seem like a more obvious choice than Twitter.
While you should be on Twitter due to its sheer user base and advertising ROI, you’ll want to keep its audience’s need to stay trendy and informed in mind as you’re creating posts and advertisements for the platform. This might help you make social content that both engages these audiences while still weaving in information about how valuable your product is.
Identifying the Right Platforms for Product Marketing
While running ads and product promotions on any social platform can help drive conversion, it’s a good idea to focus on platforms with audiences that already align well with your brand.
For example, broader audiences are actively looking for products or researching brands on Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, and Pinterest while Reddit and Twitter users tend to be more trend-focused. Similarly, if you’re marketing a B2B company, you might see a better ROI from ads on a professional network — like LinkedIn — than ads on a more consumer-friendly platform like Instagram.
Use the information provided above, and start leveraging social media for lead conversion and product marketing.


.png?width=624&name=What is a Web Crawler? (In 50 Words or Less).png)
-2.png?width=405&height=354&name=What is a Web Crawler? (In 50 Words or Less)-2.png)
-1.png?width=624&name=What is a Web Crawler? (In 50 Words or Less)-1.png)
![]()



![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-6.png)

![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-5.png)


![New Data: Instagram Engagement Report [2021 Version]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/9294dd33-9827-4b39-8fc2-b7fbece7fdb9-1.png)

![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-4.png)












![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-3.png)

![Download Now: 25 Proven Sales Email Templates [Free Access]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/be67aa79-8dbe-4938-8256-fdf195247a9c.png)