Agile marketing focuses on creating high-value deliverables by working in short bursts to achieve goals. An agile marketing process is also constantly iterated to ensure productivity and efficiency.
Measuring the success of an agile marketing process is critical as it helps monitor processes and ensures everything is on track — this is where agile metrics come in.
In this post, we’ll discuss:
What are agile metrics?
Agile metrics is a tool that helps marketing teams measure the progress and productivity of marketing activities, stay on track, and address roadblocks. Agile metrics are most effective when tailored to the specific needs of individual projects.
You can use agile metrics at both the team level and individual level. At the team level, they help assess the overall health of marketing activities and identify potential bottlenecks. At the individual level, they can help identify areas of improvement for each team member based on their progress.
Importance of Agile Metrics
Agile metrics are important because they help track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Agile metrics also:
- Increase productivity by providing visuals of project timelines so stakeholders can understand what comes next.
- Build accountability and transparency between stakeholders because everyone knows what’s expected of them and their teams.
- Improve communication between team members because agile metrics give specific insight into project progress so people can begin conversations based on metrics and data.
- Help managers and leaders identify risks and potential problems early on from historical agile metrics data, helping them correct processes and save time.
Types of Agile Metrics
There are three main types of agile metrics, and we’ll outline them below.
- Scrum Metrics: A Scrum is a process where work is done in sprints to quickly deliver small projects that make up larger projects over time. Scrum metrics analyze sprint effectiveness and show how much work was completed during a given sprint.
- Kanban Metrics: Kanban processes use visual cues to track progress over time. It usually is based on a project board that is divided into columns that represent stages in a workflow. Kanban metrics help you understand workflow effectiveness, organize and prioritize work, and the amount of time invested to obtain results.
- Lean Metrics: Lean processes help decrease the amount of time it takes from when a task or project is requested to when teams complete it. Lean metrics measure productivity and quality of work output, helping get rid of activities that don’t benefit outcomes or getting work done quickly.
Key Agile Metrics
Below we’ll go over some of the most common agile metrics.
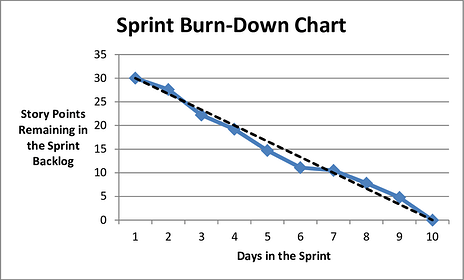
1. Sprint Burndown Chart
Type of Agile Metric: Scrum
A sprint burndown chart shows the work that remains and has already been completed in a designated sprint. It also shows the amount of work that has been completed over time.
Sprint burndown charts provide a visual for this data and can predict a team’s likelihood to complete their work in the time available.
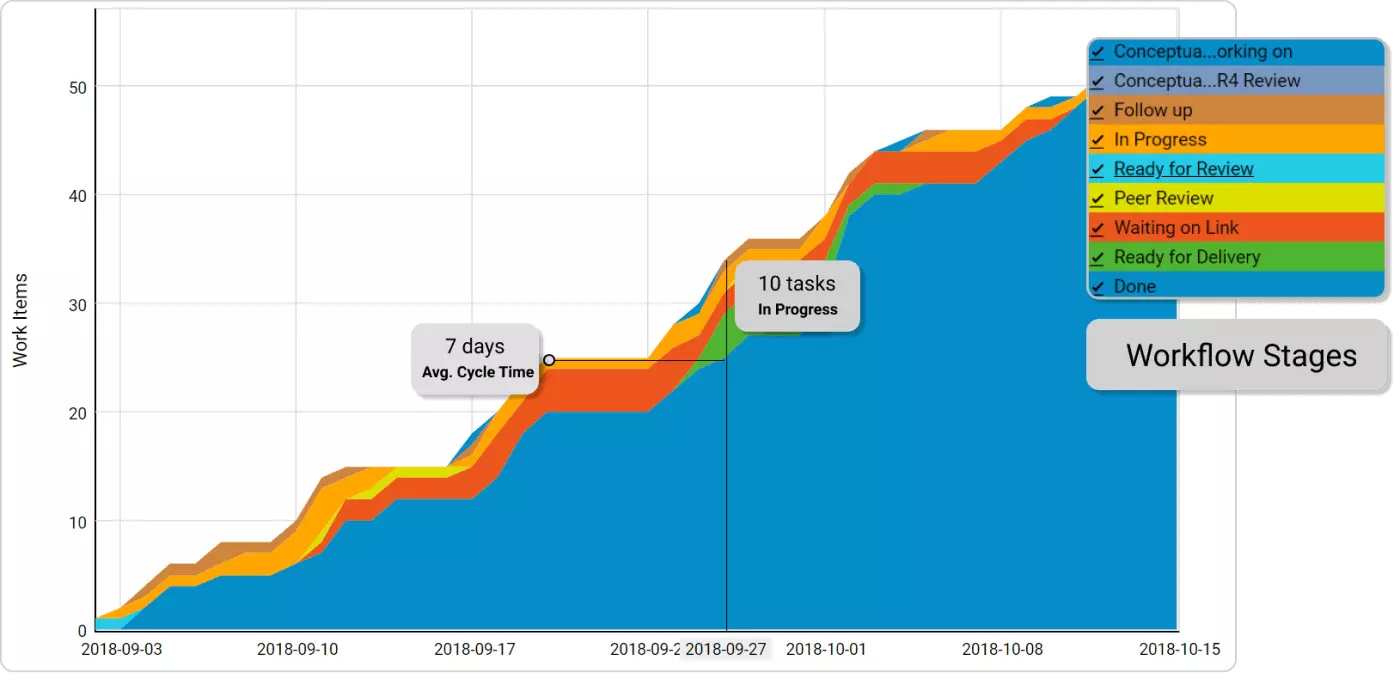
2. Cumulative Flow Diagram
Type of Agile Metric: Kanban
The cumulative flow diagram is a graphical representation of work in progress. Specifically, it displays the work already completed, the work currently in progress, and tasks that have yet to begin. The diagram helps you visualize how stable your process is and helps you identify problem areas to address.
3. Cycle Time Diagram
Type of Agile Metric: Kanban
A cycle time diagram displays the amount of time it takes to complete a task. It helps you identify areas where your process can be updated and streamlined for future productivity and understand the effects of the strategies you implement.
As your overall goal is likely to have a shorter cycle time across all projects, the diagram will help you understand the length and identify areas for improvement. Cycle time is a smaller section of the lead time metric, which we’ll discuss below.
4. Lead Time
Type of Agile Metrics: Kanban
Lead time is the time it takes for a task to be completed from start to finish. It builds off of the cycle time metric but adds on the amount of time between when a task or project was requested to when it was started.
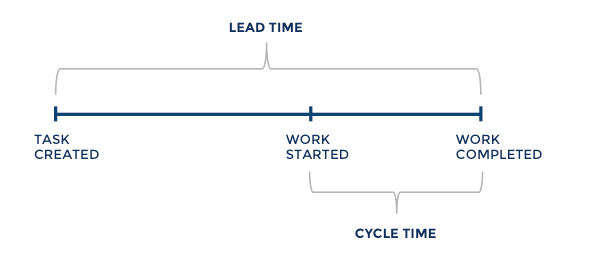
For example, you could use the lead time metric to analyze how much time it takes from when a new marketing copy is requested to when it is delivered.
5. Velocity Chart
Type of Agile Metric: Scrum
Velocity is the rate at which a team can deliver work during a sprint. It measures how fast teams complete a task and identifies whether they are on track to meet deadlines. It can also predict a team’s future abilities, helping ensure you don’t commit to a timeline you can’t achieve.
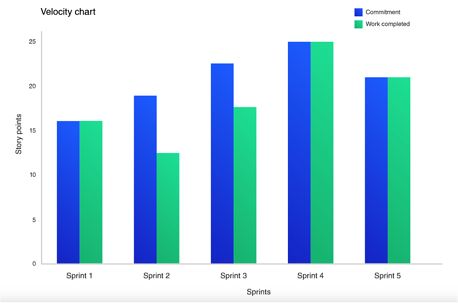
A lower velocity means it takes teams more time to complete a task, so it could be worthwhile to identify areas you can streamline to speed up the process.
6. Burn Up Chart
Type of Agile Metric: Scrum
A burn-up chart tracks progress over time. The graph features two lines, one that displays the projected amount of work and another that shows actual work completed.
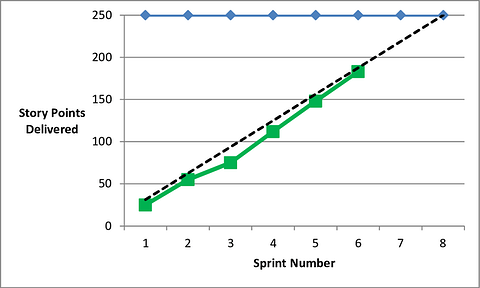
This metric helps you compare expectations to how much work is delivered, which can help you understand team efficiencies and identify areas for improvement.
The right agile metric helps you and your teams stay productive and focused.
Choosing an agile metric depends on the specific needs of your marketing activities. Once you choose one, you’ll get a bigger picture of your team’s productivity and marketing processes, helping you identify roadblocks, optimize your strategies, and meet your business goals.
![]()

![→ Free Download: Free Marketing Reporting Templates [Access Now]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/0d883e85-c2e5-49bb-bef2-bfddb500d84b.png)
