Negative and positive feedback loops are used to draw attention to significant product or company issues. These types of feedback loops use customer or employee complaints to create long-term product or workplace solutions.
Here, we’ll dive into the definitions of negative and positive feedback loops, explain their benefits for your business, and provide examples and best practices, so you can ensure your company is using constructive customer and employee feedback to cultivate higher customer retention and a happier workplace.
The Definition of a Negative Feedback Loop
A negative feedback loop is a process where a company listens to customers’ complaints or grievances, and then uses that feedback to improve their products or customer service. It’s considered a loop because customers’ feedback (output) is used as constructive input on a redesign of their product, creating a circle.
The negative feedback loop benefits both businesses and customers. Namely, customers feel valued and respected by the business and are more likely to become long-term advocates for the brand, and the business’s design is improved to increase customer satisfaction.
Below, we analyze the three key benefits of a negative feedback mechanism for a business.
Benefits of Negative Feedback Loops
1. Product/Service Improvement
Negative feedback loops are essential for product and service improvement. Companies, especially in the software development niche, often struggle with product roadmaps and prioritizing features. This process can drain a lot of the company’s time and resources.
In these situations, negative feedback loops can act as a shortcut. By directly using customer feedback, brands can quickly identify areas where their products and services underperform and address these issues with their R&D teams.
Continuously improving product features and offerings also helps companies stay up-to-date and competitive. Brands can receive feedback directly using surveys and questionnaires, or indirectly using various methods such as tracking social mentions, which provides insights from public discussions and online conversations about their products or services.
A great example of a brand that uses indirect customer feedback is Slack. Even as the company grew, they prioritized the end-user experience and engaged with customers to understand their needs and preferences. Using a negative feedback loop, the Slack team pays close attention to feedback, even if customers do not explicitly request changes.
This has helped the platform to continue to expand. As Stewart Butterfield, CEO and co-founder of Slack expresses: “So it’s usually not direct … Instead, we look at how people are using it [Slack]. What problems they’re encountering. What they’re asking us about. Often, people, when they have questions, are either asking for clarification for how something works, or they’re asking for something new.
They might not be doing it directly. And so you have to learn how to interpret that. People aren’t necessarily perfect at telling you exactly what they want or what they need. But they are perfect at being satisfied or dissatisfied with something. And if you learn how to interpret and how to listen and how to respond, you can use customer feedback to create a world-leading product.”
2. Customer Retention
Using customer feedback loops is one of the best strategies to retain customers. This proactive approach allows businesses to improve their relationships with customers, fix problems, and turn them into loyal customers over time.
Negative feedback can help businesses identify areas for improvement and take highly targeted actions to solve issues. When a company takes action to address these problems, customers are more likely to be happy and stay loyal.
Negative feedback loops can also help companies identify internal weaknesses and inefficiencies, enabling them to make necessary tweaks to improve customer satisfaction and retention.
The important thing here is persistence. Feedback loops can be slow in nature, but businesses willing to invest time and energy into them will see results. For example, Wajax focused on converting detractors into promoters by understanding customer feedback and their sentiments, achieving a 100% follow-up rate with dissatisfied customers
3. Minimized Negative Word of Mouth
Negative feedback loops serve as a buffer against the spread of negative Word of Mouth. They let companies fix issues quickly and prevent customer trust erosion.
Neglecting upset customers can be costly. In fact, 26% of people won’t do business with a brand if they hear a negative story about it from a friend or family member. Being on the lookout for negative customer experiences to address them quickly can mitigate dissatisfaction before it escalates into a PR crisis. Showing customers that their concerns are taken seriously will make them less likely to complain to potential other customers.
To explore successful negative feedback loops in more depth, let’s take a look at some examples.
Negative Feedback Loop Examples
1. Hubspot
Hubspot teams listen to customer feedback via in-app surveys that measure user satisfaction with our CRM platform and new features.
These surveys include multiple-choice, short questions, and ratings to ensure we collect feedback without inconveniencing customers. That’s how we guarantee our CRM platform is aligned with marketers’ and sales professionals’ needs.
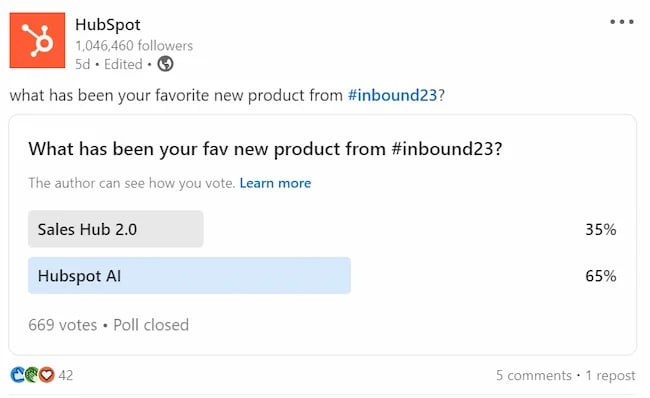
We also run polls on social media (X and LinkedIn) to understand customer intent toward our new products, compared to the competition, like the survey below:
2. Best Buy
Best Buy, the world’s largest consumer electronics retailer, effectively uses a negative feedback loop to improve their customers’ experience.
In 2010, Best Buy created a research tool, called VOCE (Voice of Consumers Through Employees), and used it to collect customer feedback and complaints.
After they collected customer feedback via VOCE, Best Buy took immediate and drastic steps to improve their service model. Among other things, they streamlined their mobile pickup orders, separated the Customer Service and Geek Squad so customers weren’t confused about where to go for which service, and created a “Geek Squad Lounge” so customers could find one-on-one help before leaving the store.
Ultimately, Best Buy saved money and guesswork by listening to their customers and strategically improving areas their customers cared about most. If, instead of a negative feedback loop, Best Buy used market research, they might not have been as effective in targeting aspects of their service most directly impacting their customers.
3. Trader Joe’s
Trader Joe’s, a grocery chain, ranked in second place in 2023 for the grocery store with a popularity score of 63%, ahead of Kroger and 7-Eleven. To maintain that high standard of customer satisfaction, Trader Joe’s doesn’t employ traditional customer service methods, like service reps manning phones.
Instead, Trader Joe’s puts a strong emphasis on in-person interaction between employees and customers. Their retail staff spends most of the day on the floor, interacting with customers and immediately responding to their needs.
Trader Joe’s employees’ attention to human interaction is necessary for impressive customer service. Trader Joe’s often goes above and beyond to respond to any negative feedback. For instance, when Marynne Aaronson requested her favorite soy ice cream cookie in their Reno, Nevada branch, they stocked up on it just for her. In Phoenix, Trader Joe’s opened before nine a.m. so the Phoenix customers could shop earlier when they wanted.
Those one-off experiences aren’t necessarily easily replicable, but they’re hugely influential for creating long-term customers.
The Definition of a Positive Feedback Loop
A positive feedback loop is a process where a company listens to employees’ complaints and suggestions and uses that feedback to improve internal structure and workplace satisfaction. As a result of employee happiness, the company is then able to increase their profits. It’s considered a loop because employees’ feedback (output) is used as input on a restructuring of the work culture, creating a circle.
A positive feedback loop, essentially, focuses on employees’ input to make the workplace better — as opposed to a negative feedback loop, which focuses on customers’ input to make the product better.
A positive feedback loop can be a formal or informal process, in which you collect employee feedback on their overall work satisfaction, and respond to that feedback to make your employees happier.
A positive feedback loop is essential for your business’s long-term success. Having happier employees is valuable, but not just for employee retention — it’s also critical for your company’s financial success. In an excerpt from Noelle C. Nelson’s book, Make More Money by Making Your Employees Happy, she found stock prices for Fortune’s “100 Best Companies to Work For” rose an average of 14% per year since 1998 — compared to six percent rise since 1998 for the market in general. Ultimately, happy employees stay longer and do better work.
Now, let’s delve into the three key benefits of a positive feedback mechanism for a business.
Benefits of Positive Feedback Loops
1. Boosted Workplace Morale
Positive feedback loops play an important role in boosting the morale of your employees because people see that their complaints and suggestions are taken seriously by the management.
And that management tries to improve the workplace, be it physically like new equipment or mentally by fostering a new, more empathetic culture among the leadership.
This validation encourages further dedication, so it’s no surprise that today 40% of professionals pick a new job based on the company culture.
2. Reduction in Employee Turnover
Companies that actively seek and incorporate regular feedback from their employees experience 14.9% lower turnover rates compared to ones that do not engage employees in the feedback process.
Positive feedback loops help greatly in reducing employee turnover because when people see that their issues are resolved quickly and the company is always eager to improve things, their dedication and satisfaction increase as well.
3. Enhanced Collaboration Among Teams
In workplaces where achievements are recognized and team members openly share what they’ve learned from challenging situations, it helps create a culture where everyone shares common values and teams work together more effectively.
It’s crucial to take action based on the feedback you receive from your employees, whether they’re expressing challenges in working together or praising their colleagues for excellent performance. Resolving issues and acknowledging hard work can not only improve workplace morale but also strengthen team cohesion and collaboration across teams.
A positive feedback mechanism can work as a control center that helps you monitor your employees’ productivity, engagement, and well-being. Now, let’s dive deeper into examples of companies with the finest positive feedback loops.
Positive Feedback Loop Examples
1. Microsoft
In 2014, Microsoft hired a new CEO, Satya Nadella, to deal with Microsoft’s toxic work culture. The high pressure and intense internal competition at Microsoft had turned employees against each other. The employees no longer felt united.
After Satya Nadella was hired, his first major project was restructuring the company to alleviate the competition between departments. To tackle this, he asked every employee to re-focus on three common goals. He outlined these goals in an email sent to his employees, along with his new mission statement for Microsoft’s culture: “Team, I believe that we can do magical things when we come together with a shared mission, clear strategy, and a culture that brings out the best in us individually and collectively.”
Satya Nadella ended his email to Microsoft employees with this remark: “I believe that culture is not static. It evolves every day based on the behaviors of everyone in the organization.”
Nadella used employee feedback to improve internal structure and unify the company. Now, Microsoft doesn’t operate under divided teams with competing goals. Instead, each product falls under one vision, so employees can happily share responsibilities and work together.
2. Southwest Airlines
Southwest Airlines, a U.S airline, first started flying in 1971 — at the time, their vision was “to make flying affordable enough that anyone could fly.”
Katie Coldwell, Director of Communications at Southwest Airlines, said, “Once we achieved this mission, it would have been easy to step back and say, ‘Okay, we’ve done it, we’re done.’ But we didn’t. We kept aspiring for something greater.” Now, the Southwest Airlines mission statement is: “to become the world’s most loved, most flown, and most profitable airline.”
While it might’ve been easy to remain loyal to their old mission, Coldwell explained it was important for Southwest to outline a deeper purpose in their mission to inspire employees and make them feel like they were making a difference. This is more important than ever. With the rise of quiet quitting and 6 out of 10 employees feeling psychologically disengaged from work, giving your employees a purpose and the sense that they can contribute to the world is necessary to reverse this effect. To increase a sense of purpose in the workplace, Coldwell encourages companies to ask their employees — “What is the value you bring to the world?”
Southwest Airlines has been listed on Glassdoor’s Best Places to Work for five consecutive years, from 2018 to 2023. Their flexibility and openness to change, despite being an older and well-established business, enables them to grow and continually inspire employees.
3. Adobe
Adobe, the famous designing software company, is among Fortune’s 2023 List of the 100 Best Companies to Work For. The company has been winning its place on that list for two decades now, making Adobe a dream workplace.
But how did they accomplish it? Adobe listens to their employee feedback every day.
In the early ‘10s, the company ditched annual progress reviews and embraced frequent check-in meetings. In these meetings manager and employee can discuss project progress and most importantly exchange feedback, when it’s fresh!
The drawback with annual reviews was that people had to wait until the end of the year to share their feedback on their collaboration with colleagues, highlight their progress, or address red flags.
Adobe took that concern into consideration and came up with the solution of frequent check-in meetings — now held online due to Adobe’s hybrid work model — that will give each employee the chance to communicate their successes and grievances to their manager often and early.
Also, Adobe offers access to real-time feedback with dedicated dashboards, so that employees can give constructive feedback to their colleagues in real time that reinforces their culture of continuous learning and improvement.
How to Gather Your Feedback
If you’re ready to use a negative feedback loop to improve your own product or service, take a look at our Customer Feedback Strategy guide. You might choose a survey, an NPS, or a feature request board to collect valuable information from customers — or, depending on your business’s onboarding process, you could collect product feedback when you speak with customers.
If you’re ready to use a positive feedback loop to improve employee satisfaction, consider some of the steps Microsoft,Southwest Airlines, and Adobe took to make their employees happy. Perhaps, you could try collecting feedback via email or department leaders or adopt anonymous feedback systems like the Employee Net Promoter System (ENPS).
Ultimately, there’s nothing better for your business than happy customers and happy employees, and both of these loops are critical for achieving both.
Feedback Loop Best Practices
Prioritize Clear and Open Communication
8 of 10 American employees say communication at work heavily affects how they feel about their jobs. Open and clear communication stands as the backbone of operational success in business. It eliminates ambiguity, creates trust, and ensures that all employees are aligned with the company’s goal and culture.
Feedback loops are a critical tool for improving performance and productivity in any organization. However, for feedback loops to be effective, they must be based on clear and open communication.
Open communication means that everyone feels comfortable sharing their thoughts and ideas, even if they are negative or critical. It also means that everyone is willing to listen to feedback from others, without getting defensive.
A clear communication means that the feedback is
- Specific
- Actionable
- Timely
It should also be delivered in a way that is respectful and constructive.
When clear and open communication is prioritized, feedback loops can be a powerful tool for driving positive change. They can help to identify areas for improvement and build stronger bonds in your company.
Remember, businesses with an established open communication feedback loop can anticipate challenges, have higher productivity rates, facilitate collaboration, and ensure that customers and employees feel valued and heard.
Automating Feedback Processes
Collecting and analyzing feedback can be time-consuming and energy-graining. Automated systems can instantly capture and analyze your customer and employee feedback, ensuring you provide immediate responses.
There are a number of ways to automate feedback processes, including:
- Using survey software to automatically send out surveys and collect responses.
- Using chatbots to collect feedback in real time.
- Integrating feedback data with other systems, such as CRM or analytics platforms, makes it easier to track and analyze feedback.
Using these tools helps you mitigate risks, have quick reflexes, and prevent crises before they escalate.
Choosing the Right Channels
For feedback loops to work effectively, it’s important to choose the right channels. This will vary depending on the specific situation. However, there are a few things to keep in mind when choosing channels:
- The target audience: Who are you trying to reach with your feedback loops? The channels you choose should be accessible and convenient for your target audience.
- The type of feedback: What kind of feedback are you hoping to get? The channels you choose should be appropriate for the type of feedback you are looking for.
- The desired level of detail: How much detail do you need from your feedback? The channels you choose should be able to capture the level of detail you need.
- The cost: How much are you willing to spend on feedback loops? The channels you choose should be affordable for your budget.
Here are some examples of different channels that can be used for feedback loops:
- Surveys
- Interviews
- Focus groups
- Social media
- Customer support
Integrate Feedback into Strategic Planning
Infusing feedback into strategic planning is indispensable for sustainable growth. By actively incorporating customer and employee insights, businesses can craft strategies that are both responsive and forward-thinking.
This alignment ensures that resources are efficiently directed towards areas of genuine need and opportunity.
Categorize Your Feedback
Segment your feedback based on its source, relevance, and impact. Prioritize feedback from loyal customers, high-value clients, or employees with expertise in critical areas. Another way to segment feedback is by the stage of the customer journey or by the department within your organization.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Feedback
Distinguish between quantitative data (e.g., survey ratings, analytics) and qualitative feedback (e.g., comments, suggestions). Both types offer unique insights. Quantitative data provides statistical trends, while qualitative feedback offers in-depth context and anecdotes. Make sure you keep a balance between these two.
Consistency and Repetition
Pay attention to recurring feedback themes and patterns. Feedback that consistently emerges across different sources or time periods is likely more important and valuable.
Acknowledging and Rewarding Feedback
This shows that the feedback is valued and appreciated, and it encourages your employees and customers to continue giving feedback. There are many ways to acknowledge and reward feedback, such as:
- Thanking the person for their feedback.
- Giving them a specific example of how their feedback was helpful.
- Recognizing their efforts in a public forum.
- Offering them a small reward, such as a gift card or a certificate of appreciation.
How Feedback Loops Can Help Your Team
The bottom line is that a feedback loop, positive or negative, can help your business spot room for improvement and bring a multitude of suggestions and solutions to the table.
Customers and employees need to be heard now more than ever. And your business should be on the lookout for such invaluable feedback that can only make you better.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in [Month Year] and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
![]()

![→ Click here to download leadership lessons from HubSpot founder, Dharmesh Shah [Free Guide].](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/4e634041-e1ce-4a85-8e65-aea12fc10b84.png)













![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-2.png)






![Sign up for HubSpot Academy's Ecommerce Marketing Course [Free Online Course]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/44a5e5f7-2ddc-4ef0-9b20-d744ed2777d0.png)

![Download Now: Free Marketing Plan Template [Get Your Copy]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/aacfe6c7-71e6-4f49-979f-76099062afa0-5.png)
