Perhaps you’ve spent the last quarter performing a SWOT analysis on your marketing efforts and identifying your priorities as you grow your brand. Maybe you’ve even built your entire marketing strategy.
It’s good to know what your goals are and have a big-picture understanding of how you’ll achieve them. After all, there’s no point in executing tasks without reasons for doing so.
At the same time, putting your marketing strategy into play is different than creating that strategy. It’s the channels, techniques, and tactics that help realize the vision. In addition, marketing a brand online has become much more nuanced and complex with many techniques for reaching and resonating with audiences.
To help you learn about the most effective marketing techniques around today, we’ve rounded up the best ones to add to your digital marketing toolbox.
Branding and Awareness Techniques
1. Brand Storytelling
Purpose: Capture Attention
In the neuroscience field, researchers have proven that storytelling is the best way to capture people’s attention, bake information into their memories, and resonate emotionally with them. The human brain is programmed to crave, seek out, and respond to well-crafted narrative — that’ll never change.
If you have an About page on your website that functions only to say what you do and who you do it for, crafting a compelling narrative is a great way to uplevel that page and resonate with your readers. For maximum effectiveness, consider following a storytelling framework such as Simon Sinek’s Find Your Why methodology, Donald Miller’s Storybrand, or the classic Hero’s Journey.
And storytelling doesn’t just have to live on your About page.
Just like your favorite Netflix show, you can craft a series on YouTube to entice your viewers to subscribe to your updates. This can get your audience more excited for your show’s newest season than they currently are for the latest season of Stranger Things.
Before you green light another slew of listicles, how-to posts, and ultimate guides, remember how powerful storytelling is and consider crafting a story chock-full of conflict, surprise, and emotion that your viewers will relate to your brand, regardless of the channel you’re targeting them on.
2. Digital PR
Purpose: Reach New Audiences
the group chat when you get a link in a huge publication pic.twitter.com/jdKVhLdA1C
— Digital PR Memes (@DigitalPRMemes)
June 22, 2021
The average amount of time spent on social media was 145 minutes per day in 2020, an increase from the previous year. Needless to say, people spend more time on social media than ever before. And public relations professionals are pivoting their strategy from solely focusing on placing their stories in news outlets’ publications to concentrating on driving traffic to their websites and social media profiles too.
In order to successfully pitch your stories to journalists and news outlets nowadays, you need to account for the content that performs well on their social media profiles and their publication. So before you pitch your story, make sure it’s relevant and interesting to the news outlet’s social audience.
3. The Surround Sound Method
 An ad’s effectiveness increases the more times it’s been seen by a prospect. It’s also pretty safe to say that any marketing asset’s effectiveness increases the more it’s seen.
An ad’s effectiveness increases the more times it’s been seen by a prospect. It’s also pretty safe to say that any marketing asset’s effectiveness increases the more it’s seen.
This is a fact previously alluded to in this post anytime the word “touchpoints” comes up.
The surround-sound methodology takes this idea and amplifies it by challenging the notion that your owned channels and assets are not enough to create true brand awareness. You should also appear everywhere else someone goes to consider products. For example:
- Review websites
- The social timelines of prominent influencers
- Featured in the media they consume (articles, videos, podcasts)
According to Alex Birkett, Sr. Growth Marketing Manager at HubSpot, if you can “get lots of people to talk about you favorably, preferably around the same time,” you can generate quite a bit of brand awareness.
4. Brand Extensions
Purpose: Expand Into Tangential Markets for Increased Awareness

Big companies often extend their brand to develop new products in industries that they don’t have any market share in. These initiatives are called brand extensions, and they allow companies to leverage their brand awareness and equity to create more revenue streams. For example, Reese’s entering the cereal market with their peanut butter and chocolate “Reese’s Puffs” product.
Historically, the most successful brand extensions are the ones that closely tie to the company’s flagship product or core brand, like Gerber’s baby clothes and Dole’s frozen fruit bars. By entering tangential markets that can preserve your brand’s unique associations and perceived quality, you can develop new products that consumers intuitively understand the benefits of, even though they’ve never seen them on a shelf.
On the flip side, a company can also exploit its brand and, in turn, damage it. If they develop a product in a market that isn’t closely tied to their flagship product or core brand, audiences might attach undesirable associations to a brand, weaken its existing associations, and hurt its established products’ perceived quality.
Audience Engagement Techniques
5. Podcasting
Purpose: Leverage Audio Content and Reach New Audiences
Technically, audio is more of a media type or channel than a technique, but according to a content format study conducted by Edison Research and Triton Digital, people age 12 and older are listening to online audio content at unprecedented levels. On average, people spend 17 hours per week tuning into their favorite podcasts, online radio shows, and audiobooks.
Needless to say, the demand for audio content has exploded, but that doesn’t mean people will listen to your branded podcast just because it’s a podcast. In reality, they’ll only listen to it if it can hold their attention and, ultimately, entertain them.
Here’s where the technique part comes in: Many podcasts rely on a host/guest model. This model is wildly successful because hosts can tap into the audience that the guest brings in and vice versa. It’s a mutually beneficial arrangement so long as both sides promote effectively. That’s why it’s important to choose guests wisely and make it easy for them to promote the show and episode they appear in.
With each guest that comes on, the podcast audience grows, and so does the engagement.
6. Video Marketing
Purpose: Leverage Video Content and Reach New Audiences
Video has overtaken blogs and infographics as the number one form of media used in content strategy (HubSpot). There’s a couple reasons for this:
- It’s flexible. You can create video for YouTube, embed it on your blog, share it on social media, and more.
- It’s a different kind of organic play. Google shows videos in the SERPs (search engine results pages). YouTube is also a search engine in its own right and is the second most visited site after Google itself (Alexa).
- The engagement is rewarding. Video consumption continues to rise, outpacing television, and it’s more effective at conveying information (Biteable).
So not only are consumers looking for audio content; they’re looking for video content as well. And savvy marketers are getting ROI in the form of engagement and repurpose-ability.
7. Community Building
Purpose: Improve Long-Term Engagement and Build Authority
Speaking of engagement, the last thing you want to do is create a piece of content and then hear crickets when you promote it. One of the best ways to increase engagement and brand awareness is by building relationships with prospects, users, customers, and other individuals in the industry.
Many brands are creating digital communities on social media, online boards, and their own hosted networks/forums. With community management, you’re building relationships, giving back, and establishing yourself as an authority in the industry. It can be as simple as answering questions on Quora or cultivating a hashtag on Twitter, or it can be as complex as creating a whole support network for your product.
Either way, you’re improving the affinity your prospects and customers have with your brand.
If done correctly, your community may even expand beyond your brand and become a beneficial resource for everyone within it. For example, Women in Tech SEO, founded by Areej AbuAli, is a community focused on accelerating the careers of women in the SEO industry. The organization has a network with a discussion component, ongoing meetups, a newsletter, and more.
8. Contextual Marketing
Purpose: Improve Website Engagement With Personalized Content

Contextual marketing is the practice of serving up personalized website content to visitors according to their stage of the buyer’s journey. The idea is that if you can cut through the noise and serve your website visitors the content that matters the most to them, you’ll be far more successful at capturing their attention.
We can all agree that improving the experience for prospects can lead to increased effectiveness, but what does contextual marketing look like in practice?
For example, you might use dynamic CTAs that only show them offers that are relevant to them. This cuts down on the amount of useless information they’re taking in on your website and decreases banner blindness… in part because the banners they do see are helpful and relevant.
It might also mean using smart forms so that you don’t keep asking for the same information from website visitors who have cause to fill out multiple forms on your site.
Then, you might segment your database so that your leads receive email campaigns that are directly relevant to their needs based on content that they’ve already consumed on your website.
All of this resulting in a personalized, tailored journey without the pressure of going to a salesperson for it.
Techniques for Driving Traffic
9. Blog Title Optimization
Purpose: Increase Traffic to Existing Assets By Improving Click-Through Rate
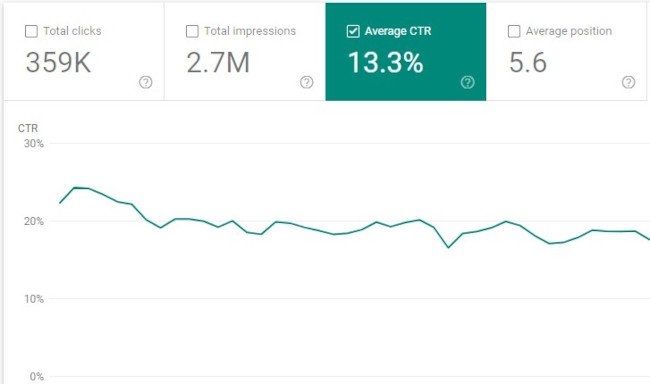 When you write a blog post, do you use the first title you came up with or do you write a few?
When you write a blog post, do you use the first title you came up with or do you write a few?
People will not get to the rest of your content until they choose to click on the headline. That’s why it’s so important to have grabby titles that resonate with your audience and compel them to click.
By increasing the effectiveness of your titles, you can increase click-through rate (and, in effect, traffic). One way to do this is by using tools like this headline analyzer to see what you can do to improve your headline.
Better yet, you can always analyze your existing blog posts to see which headlines aren’t doing enough heavy lifting. By improving the click-through rate, you’ll be able to get more traffic from that asset without a heavy editorial lift.
10. The Pillar-Cluster Model
Purpose: Drive Traffic By Establishing Topic Authority
Since people heavily rely on Google to provide accurate and relevant answers for most of their questions today, Google needs to understand the intent and context behind every single search.
To do this, Google has evolved to recognize topical connections across users’ queries, look back at similar queries that users have searched for in the past, and surface the content that best answers them. As a result, Google will deliver content that they deem the most authoritative on the topic.
To help Google recognize your content as a trusted authority on marketing, sales, and customer service topics, consider implementing the pillar-cluster model on your blog.
Essentially, the pillar-cluster model is a topic-based based content strategy. This means that you generate and organize ideas for your blog by topic.
By creating a single pillar page (an ultimate guide, for instance) that provides a high-level overview of a topic and hyperlinks to cluster pages (subtopic blog posts) that delve into the topic’s subtopics, you can signal to Google that your pillar page is an authority on the topic.
Hyperlinking all of the cluster pages to the pillar page also spreads domain authority across the cluster, so your cluster pages get an organic boost if your pillar page ranks higher, and your cluster pages can even help your pillar page rank higher if they start ranking for the specific keywords they’re targeting.
11. Historical Optimization
Purpose: Drive Traffic By Improving Existing Assets
There’s a massive hole in the market for specialized services around updating/optimizing old content.
We’ve all been creating content for years now.
The greater opportunity, and quicker time to value for agencies/contractors, is in updating…not creating.
— John Bonini (@Bonini84)
September 4, 2020
In 2015, HubSpot made a revolutionary discovery about our organic monthly blog traffic — the overwhelming majority of it came from posts published prior to that month. In fact, 76% of monthly blog views came from these old posts.
Today, the groundbreaking revelation rings louder than ever — 89% of our monthly blog views currently come from posts that were published at least six months prior, and we’ve developed an entire strategy dedicated to refreshing and republishing these historical pieces of content.
These types of blog posts are called “updates,” and they comprise 35-40% of HubSpot’s editorial calendar. By refreshing posts with new information and effectively republishing them as new blog posts, HubSpot can build upon its existing organic value that these posts have accumulated through backlinks and user engagement and double or even triple their traffic. This process also helps HubSpot optimize our blog for efficiency, decreasing the amount of new content we have to create while increasing our organic traffic and conversions.
12. Retargeting
Purpose: Recapture Lost Traffic
A lot of content marketing techniques involve attracting new audiences rather than improving the effectiveness of the audiences you’ve already acquired. That’s why retargeting earns a place on this list as a vastly underutilized tactic.
I’ll explain retargeting with a scenario: A prospect comes to an ecommerce site and checks out a product. They decide it’s not time to buy, and they leave. Retargeting allows you to remind them of their initial interest by showing them ads for the product on other sites (e.g. banner ads or Facebook ads). In effect, your ads “follow them around” the internet, increasing the likelihood that they come back to make that purchase.
13. The Skyscraper Backlinking Method
Purpose: Obtain Links for Increased Traffic and Improved SEO Signals
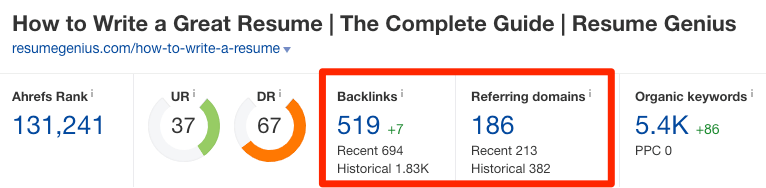
Earning high-quality inbound links from websites and pages with high authority scores is crucial for boosting your domain authority. But, unfortunately, “If you write it, they will link to it,” is not a viable SEO technique.
One method for earning high-quality links is by performing email outreach to ask other websites that have the same or higher domain or page authority score than you to link to your top content. You should also make sure your content is relevant to the referring website’s content.
More specifically, you can use Backlinko’s skyscraper method. The skyscraper method is an SEO strategy where you find content that ranks well for keywords you want to rank for and then create content that’s better than the top-ranking posts. Then, you use SEO tools to find all the sites that have linked to your competitor’s content and ask the most relevant sites to replace your competitor’s link with a link to your improved content.
Conversion and Nurturing Techniques
14. A/B Testing for CTAs
Purpose: Improve Conversion Rate on Existing Assets by Testing Variables
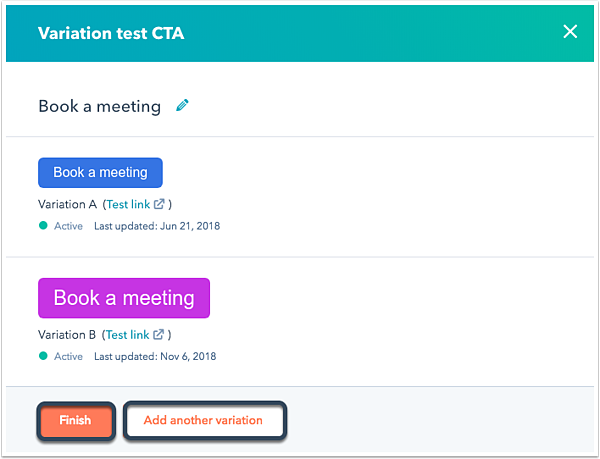
Since opt-ins are key for growing your email subscriber list, you’ll want to closely monitor the performance of your CTAs (buttons that send people to your forms) and improve on the ones that aren’t working out.
Every company has a different set of customers, so there’s no one-size-fits-all formula for designing the most optimal CTAs. To figure out which CTA design or copy will produce the best results for your company, you must experiment.
A/B testing allows you to do that experimentation between two CTAs synchronously, eliminating variables and giving you the best insight into which version performs better.
For example, you can run an experiment to test a variable such as color. Let’s say you have a red CTA and a blue CTA. A/B testing allows you to identify which ones produce better results.
To conduct an A/B test, you can use HubSpot’s A/B testing kit. With this kit, you’ll get guidelines for A/B testing, learn what variables to test, and gain access to a simple significance calculator to track your results.
A/B testing shouldn’t be confused with multivariate testing, though, which allows you to simultaneously test many variables.
15. Value-Add Emails
Purpose: Improve Engagement and Earn Goodwill During Nurturing Process
 Email is more of a channel than a tactic, but let’s start with why the channel is an important one. Did you know that Americans spend up to five hours checking their email, and the channel is by far their preferred way to receive updates from brands?
Email is more of a channel than a tactic, but let’s start with why the channel is an important one. Did you know that Americans spend up to five hours checking their email, and the channel is by far their preferred way to receive updates from brands?
At the same time, it’s projected that 319.6 billion emails will be sent and received in 2021. This means that there isn’t a lot of room for error if you want to cut through the noise when you send an email.
Since it takes a multiple touchpoints to gain the attention of prospects, persuading people to subscribe to your emails and, in turn, constantly consume your content will generate more leads and revenue for your business.
This is where the tactic part comes in. The last thing you want to do is clutter up their inbox with yet another sales email. Instead, consider emails that actually provide value along their paths to purchase.
Take the email above from HubSpot Agency Partner Yokel Local for example. It doesn’t matter if the recipient of the email is actively considering Yokel Local’s services; they still provide value that keeps their subscribers opening emails.
Growing an engaged, loyal subscriber base also speaks volumes about the quality of your content and its emotional resonance. If your prospects actively engage with your email content, it’s a clear sign that they actually value it. This contributes to their impression of your brand and serves as the touchpoints along their paths to purchase.
16. Audience Segmentation
Purpose: Create a More Personalized Experience to Improve Nurturing
In a world overflowing with digital noise, creating irrelevant or unwarranted content won’t catch anyone’s attention.
To email the right person the right content at the right time, consider leveraging audience segmentation, which separates your subscriber database into specific, accessible groups of people based on personal attributes like their demographics, psychographics, and behavioral information.
This technique allows you to increase the value of your emails (see the technique above) by ensuring that they’re more relevant to your subscribers. In other words, rather than creating messaging designed to appeal to everyone, you’ll be able to get much more specific with your messaging because you’ll have a narrower target audience.
To properly implement audience segmentation techniques into your email marketing strategy, you’ll need a CRM and marketing platform. For example, HubSpot allows you to gather information about your customers and segment contacts into lists based on that information. This makes it easy to target the right customers in your database with messaging specific to them.
17. Marketing Automation
Purpose: Enhance Efficiency of Email Campaigns
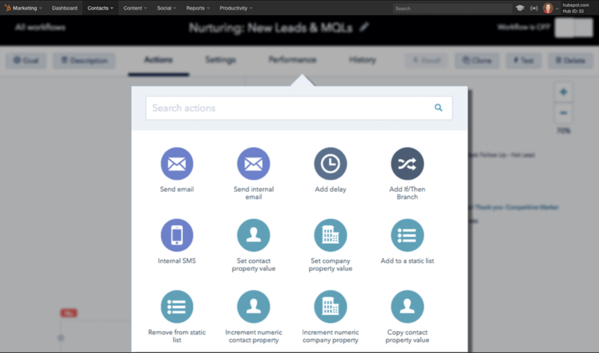
Automation is the process of using technology to eliminate manual actions and trigger repetitive or programmable functionality in an automatic way. Marketing automation applies this principle to your CRM and email marketing activities, allowing you free up time and get your message out at scale.
Instead of sending one-off emails, you can use marketing automation to initiate a sequence of emails and actions, all without you hitting the send button. Best of all, you can apply it to any of the following (and more):
- Lead nurturing campaigns
- Auto-responder sequences
- Re-engagement campaigns
- Event reminders
- Client onboarding sequences
- Up-sell campaigns
This will allow you to increase your organization’s touchpoints with a lead without tanking your productivity. To do so, you’ll first need to invest in marketing automation software.
18. Lead Scoring
Lead scoring is an automation-based technique that rates (or “scores”) your leads based on certain attributes. The idea behind it is that you’ll be able to better identify leads that are closer to a purchasing decision so that you can prioritize those leads for your marketing and sales efforts.
Some marketing automation software can perform lead scoring using AI machine learning, but many allow you to manually designate the attributes that make a marketing or sales qualified lead. Once a lead meets the criteria, they will have a higher score (and thus higher priority for more direct marketing and sales conversations).
In addition, the act of defining the criteria for lead scoring can lead to a better relationship between your marketing and sales teams. With a clear definition, your marketing team will be better focused on generating leads that meet those criteria, and your sales team will be happy with more qualified leads.
Innovation Is Key
Whether you’re developing a new marketing plan or improving on an old one, it’s important to consider new marketing techniques.
While your marketing strategy may be sound, relying on past tried-and-true methods may not be enough. As time goes on, old techniques lose competitive advantage and become table stakes. New methods will help you implement your strategic goals in new, exciting ways.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in May 2019 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
![]()



![→ Click here to access 5 free cover letter templates [Free Download]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/3f347702-d7e9-4e59-9fe4-be4cd7bad191.png)



![→ Click here to download leadership lessons from HubSpot founder, Dharmesh Shah [Free Guide].](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/4e634041-e1ce-4a85-8e65-aea12fc10b84.png)



.png?width=624&name=What is a Web Crawler? (In 50 Words or Less).png)
-2.png?width=405&height=354&name=What is a Web Crawler? (In 50 Words or Less)-2.png)
-1.png?width=624&name=What is a Web Crawler? (In 50 Words or Less)-1.png)

![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-6.png)

![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-5.png)


![New Data: Instagram Engagement Report [2021 Version]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/9294dd33-9827-4b39-8fc2-b7fbece7fdb9-1.png)

![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-4.png)












![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://i4lead.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e-3.png)
